TJ-II:Langmuir Probes: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(Updated reference links) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
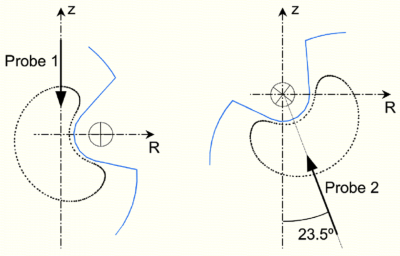
[[File:TJ-II_Langmuir.png|400px|thumb|right|Location of the reciprocating Langmuir probes at TJ-II]] | [[File:TJ-II_Langmuir.png|400px|thumb|right|Location of the reciprocating Langmuir probes at TJ-II]] | ||
[[TJ-II]] has two fast reciprocating drives for [[:Wikipedia:Langmuir probe|Langmuir probes]] (with a displacement velocity of approximately 1 m/s). | [[TJ-II]] has two fast reciprocating drives for [[:Wikipedia:Langmuir probe|Langmuir probes]] (with a displacement velocity of approximately 1 m/s). | ||
<ref> | <ref>M.A. Pedrosa et al, ''Fast movable remotely controlled Langmuir probe system'', [[doi:10.1063/1.1149350|Rev. Sci. Instrum. '''70''' (1999) 415]]</ref> | ||
<ref> | <ref>E. Calderón et al, ''On the Influence of Probe Presheath on the Measurement of Fluctuation and E × B Turbulent Transport by Langmuir Probes'', [[doi:10.1002/ctpp.200410104|Contributions to Plasma Physics '''44''', Issue 7-8 (2004) 700 - 704]]</ref> | ||
<ref> | <ref>M.A. Pedrosa et al, ''Evidence of Long-Distance Correlation of Fluctuations during Edge Transitions to Improved-Confinement Regimes in the TJ-II Stellarator'', [[doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.215003|Phys. Rev. Lett. '''100''' (2008) 215003]]</ref> | ||
Probe drive 1 is located at φ = 38.2°, R=134 cm ([[TJ-II:Sectors|sector]] D4) and probe drive 2 at φ = 195° ([[TJ-II:Sectors|sector]] B2). | Probe drive 1 is located at φ = 38.2°, R=134 cm ([[TJ-II:Sectors|sector]] D4) and probe drive 2 at φ = 195° ([[TJ-II:Sectors|sector]] B2). | ||
Revision as of 17:55, 3 April 2018
TJ-II has two fast reciprocating drives for Langmuir probes (with a displacement velocity of approximately 1 m/s). [1] [2] [3] Probe drive 1 is located at φ = 38.2°, R=134 cm (sector D4) and probe drive 2 at φ = 195° (sector B2).
Probe heads
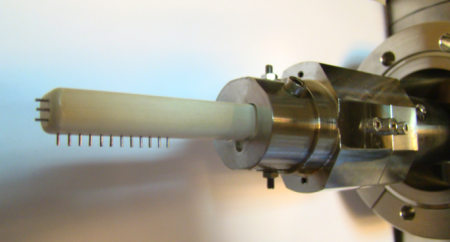
Several different heads can be mounted on the reciprocating drives: e.g., staircase Langmuir probes, a rake probe (as of 2009), or a multi-pin Langmuir probe (2010). A biasing probe has also been used.
See also
References
- ↑ M.A. Pedrosa et al, Fast movable remotely controlled Langmuir probe system, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 70 (1999) 415
- ↑ E. Calderón et al, On the Influence of Probe Presheath on the Measurement of Fluctuation and E × B Turbulent Transport by Langmuir Probes, Contributions to Plasma Physics 44, Issue 7-8 (2004) 700 - 704
- ↑ M.A. Pedrosa et al, Evidence of Long-Distance Correlation of Fluctuations during Edge Transitions to Improved-Confinement Regimes in the TJ-II Stellarator, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 (2008) 215003