Toroidal coordinates: Difference between revisions
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
J^{-1} = \det\left(\frac{\partial(\psi,\theta,\phi)}{\partial(x,y,z)}\right) = \nabla{\psi}\cdot\nabla{\theta} \times \nabla{\phi} | J^{-1} = \det\left(\frac{\partial(\psi,\theta,\phi)}{\partial(x,y,z)}\right) = \nabla{\psi}\cdot\nabla{\theta} \times \nabla{\phi} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
It can be seen that<ref> | It can be seen that <ref></ref> <math>g \equiv \det(g_{ij}) = J^2 \Rightarrow J = \sqrt{g}</math> | ||
== Flux Coordinates == | == Flux Coordinates == | ||
Revision as of 14:19, 17 August 2010
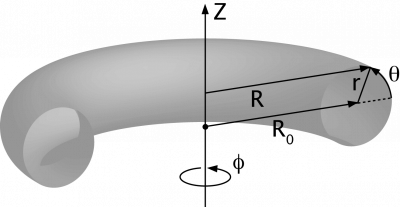
Coordinate systems used in toroidal systems:
Cartesian
(X, Y, Z) [1]
Cylindrical
(R, φ, Z), where [2]
- R2 = X2 + Y2, and
- tan φ = Y/X.
φ is called the toroidal angle (and not the cylindrical angle, at least not in the context of magnetic confinement).
Cylindrical symmetry (symmetry under rotation over φ) is referred to as axisymmetry.
Simple toroidal
(r, φ, θ), where
- R = R0 + r cos θ, and
- Z = r sin θ
R0 corresponds to the torus axis and is called the major radius, while r is called the minor radius, and θ the poloidal angle.
In order to adapt this simple system better to the magnetic surfaces of an axisymmetric MHD equilibrium, it may be enhanced by [3]
- letting R0 depend on r (to account for the Shafranov shift of flux surfaces) [4]
- adding ellipticity (ε), triangularity (κ), etc. (to account for non-circular flux surface cross sections)
Toroidal
where Rp is the pole of the coordinate system. Surfaces of constant ζ are tori with major radii R = Rp/tanh ζ and minor radii r = Rp/sinh ζ. At R = Rp, ζ = ∞, while at infinity and at R = 0, ζ = 0. The coordinate η is a poloidal angle and runs from 0 to 2π. This system is orthogonal.
The Laplace equation separates in this system of coordinates, thus allowing an expansion of the vacuum magnetic field in toroidal harmonics. [7] [8]
General Curvilinear Coordinates
Here we briefly review the basic definitions of a general curvilinear coordinate system for later convenience when discussing toroidal flux coordinates and magnetic coordinates.
Function coordinates and basis vector
Given the spatial dependence of a coordinate set we can calculate the contravariant basis vectors
and the dual covariant basis defined as
where are cyclic permutations of and we have used the notation . The Jacobian is defined below.
Any vector field can be represented as
or
In particular any basis vector . The metric tensor is defined as
Jacobian
The Jacobian of the coordinate transformation is defined as
and that of the inverse transformation
It can be seen that Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; refs with no name must have content
Flux Coordinates
A flux coordinate set is one that includes a flux surface label as a coordinate. A flux surface label is a function that is constant and single valued on each flux surface. In our naming of the general curvilinear coordinates we have already adopted the usual flux coordinate convention for toroidal equilibrium with nested flux surfaces with being the flux surface label and are -periodic poloidal and toroidal-like angles.
Different flux surface labels can be chosen like toroidal or poloidal magnetic fluxes or the volume contained within the flux surface. By single valued we mean to ensure that any flux label is a monotonous function of any other flux label , so that the function is invertible at least in a volume containing the region of interest.
Flux Surface Average
The flux surface average of a function is defined as the limit
where is the volume confined between two flux surfaces. It is therefore a volume average over an infinitesimal spatial region rather than a surface average.
Introducing the differential volume element
or, noting that , we have and we get to a more practical form of the Flux Surface Average
Note that , so the FSA is a surface integral weighted by :
Applying Gauss' theorem to the definition of FSA we get to the identity
Useful properties of FSA
Some useful properties of the FSA are
Magnetic field representation in flux coordinates
The choice of a system of flux coordinates allows to express the (nested flux-surfaces forming) magnetic field as
called the Clebsch representation. It is also an expression of in terms of the covariant basis vectors
Field lines are then given as the intersection of the constant- and constant- surfaces. The function is sometimes referred to as the magnetic field's stream function.
Magnetic
All of the above coordinate systems are fixed and axisymmetric (except the Cartesian system). By contrast, magnetic coordinates adapt to the magnetic field, and therefore to the MHD equilibrium (also see Flux surface). Magnetic coordinates simplify the description of the magnetic field. In 3 dimensions (not assuming axisymmetry), the most commonly used coordinate systems are: [9]
- Hamada coordinates. [10][11] In these coordinates, both the field lines and current lines corresponding to the MHD equilibrium are straight.
- Boozer coordinates. [12][13] In these coordinates, the field lines corresponding to the MHD equilibrium are straight.
These two coordinate systems are related. [14]
References
- ↑ Wikipedia:Cartesian coordinate system
- ↑ Wikipedia:Cylindrical coordinate system
- ↑ R.L. Miller et al, Noncircular, finite aspect ratio, local equilibrium model, Phys. Plasmas 5 (1998) 973
- ↑ R.D. Hazeltine, J.D. Meiss, Plasma confinement, Courier Dover Publications (2003) ISBN 0486432424
- ↑ Morse and Feshbach, Methods of theoretical physics, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1953 ISBN 007043316X
- ↑ Wikipedia:Toroidal coordinates
- ↑ F. Alladio, F. Chrisanti, Analysis of MHD equilibria by toroidal multipolar expansions, Nucl. Fusion 26 (1986) 1143
- ↑ B.Ph. van Milligen and A. Lopez Fraguas, Expansion of vacuum magnetic fields in toroidal harmonics, Computer Physics Communications 81, Issues 1-2 (1994) 74-90
- ↑ W.D. D'haeseleer, Flux coordinates and magnetic field structure: a guide to a fundamental tool of plasma theory, Springer series in computational physics, Springer-Verlag (1991) ISBN 3540524193
- ↑ S. Hamada, Nucl. Fusion 2 (1962) 23
- ↑ J.M. Greene and J.L Johnson, Stability Criterion for Arbitrary Hydromagnetic Equilibria, Phys. Fluids 5 (1962) 510
- ↑ A.H. Boozer, Plasma equilibrium with rational magnetic surfaces, Phys. Fluids 24 (1981) 1999
- ↑ A.H. Boozer, Establishment of magnetic coordinates for a given magnetic field, Phys. Fluids 25 (1982) 520
- ↑ K. Miyamoto, Controlled fusion and plasma physics, Vol. 21 of Series in Plasma Physics, CRC Press (2007) ISBN 1584887095