Ellipticity: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(added expression "elongation") |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
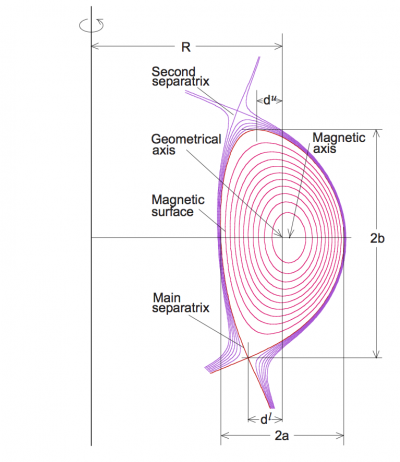
[[File:Geometry.png|400px|thumb|right|Sketch of tokamak geometry]] | [[File:Geometry.png|400px|thumb|right|Sketch of tokamak geometry]] | ||
The ellipticity refers to the shape of the poloidal cross section of the Last Closed [[Flux surface]] or [[separatrix]] of a [[tokamak]]. | The ellipticity (also referred to as elongation<ref name="Luce2013">T.C. Luce, [[doi:10.1088/0741-3335/55/9/095009|Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion '''55''' (2013) 095009 ]]</ref>) refers to the shape of the poloidal cross section of the Last Closed [[Flux surface]] or [[separatrix]] of a [[tokamak]]. | ||
Assuming<ref | Assuming<ref name="Luce2013" />: | ||
* ''R<sub>max</sub>'' is the maximum value of ''R'' along the LCFS or separatrix. | * ''R<sub>max</sub>'' is the maximum value of ''R'' along the LCFS or separatrix. | ||
* ''R<sub>min</sub>'' is the minimum value of ''R'' along the LCFS or separatrix. | * ''R<sub>min</sub>'' is the minimum value of ''R'' along the LCFS or separatrix. | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 29 May 2020
The ellipticity (also referred to as elongation[1]) refers to the shape of the poloidal cross section of the Last Closed Flux surface or separatrix of a tokamak.
Assuming[1]:
- Rmax is the maximum value of R along the LCFS or separatrix.
- Rmin is the minimum value of R along the LCFS or separatrix.
- Zmax is the maximum value of Z along the LCFS or separatrix.
- Zmin is the minimum value of Z along the LCFS or separatrix.
- a is the minor radius of the plasma, defined as (Rmax - Rmin)/2.
The ellipticity is then defined as follows:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 T.C. Luce, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 55 (2013) 095009