Triangularity
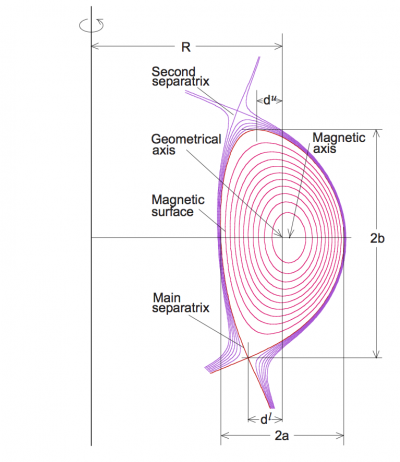
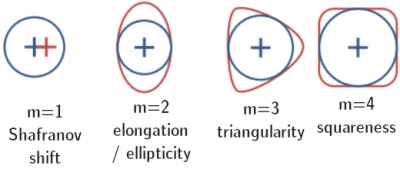
The triangularity refers to the shape of the poloidal cross section of the Last Closed Flux surface (LCFS) or separatrix of a tokamak. Assuming[1]:
- Rmax is the maximum value of R along the LCFS or separatrix.
- Rmin is the minimum value of R along the LCFS or separatrix.
- Rgeo is the geometric major radius, defined as (Rmax + Rmin)/2.
- a is the minor radius of the plasma, defined as (Rmax - Rmin)/2.
- Rupper is the major radius of the highest vertical point of the LCFS or separatrix.
- Rlower is the major radius of the lowest vertical point of the LCFS or separatrix.
The upper triangularity is then defined as follows:
and similar for δlower. The overall triangularity is defined as the mean of δupper and δlower.
Triangularity, especially the triangularity opposite the dominant X-point (so upper triangularity for a lower null plasma), influences the stability and character of the pedestal and ELMs.[2]
Some devices (TCV and DIII-D) can form plasma cross sections with negative triangularity (the X-points are pushed to larger than the center of the plasma), which makes H-mode difficult or impossible to access but improves performance of the L-mode.[3]