Ellipticity: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with "The ellipticity refers to the shape of the poloidal cross section of the Last Closed Flux surface or separatrix of a tokamak. It is defined as the total vertical h..." |
Add a figure with simple illustrations of Shafranov shift, elongation, triangularity, and squareness. |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The ellipticity refers to the shape of the poloidal cross section of the Last Closed [[Flux surface]] or [[separatrix]] of a [[tokamak]]. | [[File:Geometry.png|400px|thumb|right|Sketch of tokamak geometry]] | ||
[[File:Cross_section_1shift_2elong_3triang_4square.png|400px|thumb|right|Illustration of the m=1,2,3, and 4 perturbations to a tokamak plasma cross section. Ellipticity/elongation is the m=2 perturbation (second from the left).]] | |||
The ellipticity (also referred to as elongation<ref name="Luce2013">T.C. Luce, [[doi:10.1088/0741-3335/55/9/095009|Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion '''55''' (2013) 095009 ]]</ref>) refers to the shape of the poloidal cross section of the Last Closed [[Flux surface]] or [[separatrix]] of a [[tokamak]]. | |||
Assuming<ref name="Luce2013" />: | |||
* ''R<sub>max</sub>'' is the maximum value of ''R'' along the LCFS or separatrix. | |||
* ''R<sub>min</sub>'' is the minimum value of ''R'' along the LCFS or separatrix. | |||
* ''Z<sub>max</sub>'' is the maximum value of ''Z'' along the LCFS or separatrix. | |||
* ''Z<sub>min</sub>'' is the minimum value of ''Z'' along the LCFS or separatrix. | |||
* ''a'' is the minor radius of the plasma, defined as ''(R<sub>max</sub> - R<sub>min</sub>)/2''. | |||
The ellipticity is then defined as follows: | |||
:<math> \kappa = (Z_{max}-Z_{min})/2a</math> | |||
Higher elongation is beneficial for fusion performance, but comes with increased vertical instability growth rate and thus increased risk of vertical displacement event (VDE) type disruptions.<ref>D.A. Humphreys, et al., ''Experimental vertical stability studies for ITER performance and design guidance'' [[doi:10.1088/0029-5515/49/11/115003|Nucl. Fusion '''49''' (2009) 115003]]</ref> | |||
Because of vertical stability constraints, <math>\kappa</math> is usually limited to a value close to about 1.8. | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Triangularity]] | * [[Triangularity]] | ||
* [[Toroidal coordinates]] | |||
* [[Effective plasma radius]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:47, 30 March 2023
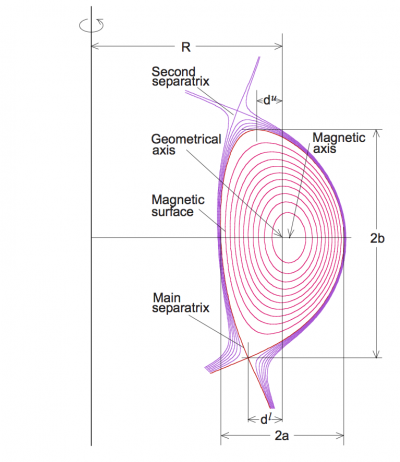
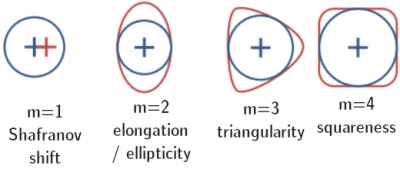
The ellipticity (also referred to as elongation[1]) refers to the shape of the poloidal cross section of the Last Closed Flux surface or separatrix of a tokamak.
Assuming[1]:
- Rmax is the maximum value of R along the LCFS or separatrix.
- Rmin is the minimum value of R along the LCFS or separatrix.
- Zmax is the maximum value of Z along the LCFS or separatrix.
- Zmin is the minimum value of Z along the LCFS or separatrix.
- a is the minor radius of the plasma, defined as (Rmax - Rmin)/2.
The ellipticity is then defined as follows:
Higher elongation is beneficial for fusion performance, but comes with increased vertical instability growth rate and thus increased risk of vertical displacement event (VDE) type disruptions.[2] Because of vertical stability constraints, is usually limited to a value close to about 1.8.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 T.C. Luce, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 55 (2013) 095009
- ↑ D.A. Humphreys, et al., Experimental vertical stability studies for ITER performance and design guidance Nucl. Fusion 49 (2009) 115003