Toroidal coordinates: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with '400px|thumb|right|A toroidal co-ordinate system Co-ordinate systems used in toroidal systems: == Eulerian == (''X'', ''Y'', ''Z'') == Cylind…' |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 10:56, 13 September 2009
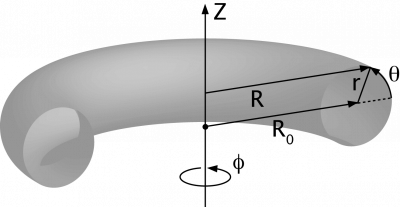
Co-ordinate systems used in toroidal systems:
Eulerian
(X, Y, Z)
Cylindrical
(R, φ, Z), where
- R2 = X2 + Y2, and
- tan φ = Y/X.
Simple toroidal
(r, φ, θ), where
- R = R0 + r cos θ, and
- Z = r sin θ
(R0 corresponding to the axis of the torus)
Toroidal
where Rp is the pole of the coordinate system. Surfaces of constant ζ are tori with major radii R = Rp/tanh ζ and minor radii r = Rp/sinh ζ. At R = Rp, ζ = ∞, while at infinity and at R = 0, ζ = 0. The coordinate η is a poloidal angle and runs from 0 to 2π. This system is orthogonal.
Magnetic
See Flux surface.