W7-X: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→References) |
|||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
* H.-S. Bosch et al, ''Technical challenges in the construction of the steady-state stellarator Wendelstein 7-X'', [[doi:10.1088/0029-5515/53/12/126001|Nucl. Fusion '''53''' (2013) 126001]] | * H.-S. Bosch et al, ''Technical challenges in the construction of the steady-state stellarator Wendelstein 7-X'', [[doi:10.1088/0029-5515/53/12/126001|Nucl. Fusion '''53''' (2013) 126001]] | ||
* D. Clery, ''Feature: The bizarre reactor that might save nuclear fusion'', [[doi:10.1126/science.aad4746|Science, 21 October 2015]] | * D. Clery, ''Feature: The bizarre reactor that might save nuclear fusion'', [[doi:10.1126/science.aad4746|Science, 21 October 2015]] | ||
* O. Neubauer et al, ''Diagnostic setup for investigation of plasma wall interactions at Wendelstein 7-X'', [[doi:10.1016/j.fusengdes.2015.06.102|Fusion Engineering and Design '''96-97''' (2015) 891-894]] | |||
* T. Sunn Pedersen et al, ''Plans for the first plasma operation of Wendelstein 7-X'', [[doi:10.1088/0029-5515/55/12/126001|Nucl. Fusion '''55''' (2015) 126001]] | |||
* M. Krychowiak et al, ''Overview of diagnostic performance and results for the first operation phase in Wendelstein 7-X'', [[doi:10.1063/1.4964376|Review of Scientific Instruments '''87''' (2016) 11D304]] | |||
* R.C. Wolf et al, ''Major results from the first plasma campaign of the Wendelstein 7-X stellarator'', [[doi:10.1088/1741-4326/aa770d|Nucl. Fusion '''57''' (2017) 102020]] | |||
* D. Hathiramani et al, ''Upgrades of edge, divertor and scrape-off layer diagnostics of W7‐X for OP1.2'', [[doi:10.1016/j.fusengdes.2018.02.013|Fusion Engineering and Design '''136A''' (2018) 304-308]] | |||
* A. Dinklage et al, ''Magnetic configuration effects on the Wendelstein 7-X stellarator'', [[doi:10.1038/s41567-018-0141-9|Nature Phys '''14''' (2018) 855–860]] | |||
* R.C. Wolf et al, ''Performance of Wendelstein 7-X stellarator plasmas during the first divertor operation phase'', [[doi:10.1063/1.5098761|Physics of Plasmas '''26''' (2019) 082504]] | |||
[[Category:Toroidal confinement devices]] | [[Category:Toroidal confinement devices]] | ||
Revision as of 06:39, 3 April 2023
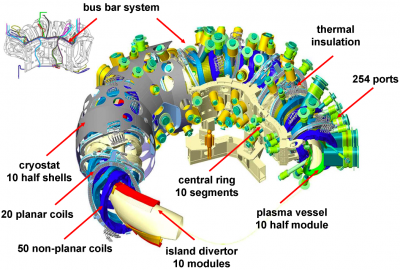
Wendelstein 7-X (W7-X) is an experimental stellarator currently being built in Greifswald, Germany by the Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik (IPP). W7-X is an optimized stellarator, i.e. the magnetic field has been tailored to meet several physical optimization criteria.
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Major radius, R0: | 5.5 | m |
| Minor radius, a: | 0.53 | m |
| Plasma volume, V: | 30 | m3 |
| Non-planar coils: | 50 | |
| Planar coils: | 20 | |
| Number of ports: | 254 | |
| Rotational transform, ι/2π: | 5/6-5/4 | |
| Magnetic field on axis, B0: | <3 | T |
| Stored energy, W: | 600 | MJ |
| Heating power, P: | 15-30 | MW |
| Pulse length: | 30 | min |
| Machine height: | 4.5 | m |
| Machine diameter: | 16 | m |
| Machine mass: | 725 | t |
Optimization criteria
- Feasible modular coils
- Good, nested magnetic surfaces
- Good finite-β equilibria
- Good MHD stability
- Small neoclassical transport
- Small bootstrap current
- Good confinement of fast particles
See also
References
- H. Wobig, The theoretical basis of a drift-optimized stellarator reactor, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 35 (1993) 903
- J. Nührenberg et al., Trans. Fusion Technology 27 (1995) 71
- C. Nührenberg, Global ideal magnetohydrodynamic stability analysis for the configurational space of Wendelstein 7–X, Phys. Plasmas 3 (1996) 2401
- V. Erckmann et al, The W7-X project: scientific basis and technical realization, Fusion Engineering 6-10 (1997) 40
- M. Wanner and the W7-X Team, Design goals and status of the WENDELSTEIN 7-X project, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 42 (2000) 1179
- M. Wanner et al, Design and construction of WENDELSTEIN 7-X, Fusion Engineering and Design 56-57 (2001) 155-162
- M. Wanner et al, Status of WENDELSTEIN 7-X construction, Nucl. Fusion 43 (2003) 416
- M. Wanner and the W7-X Team, Construction and assembly of WENDELSTEIN 7-X, Fusion Engineering and Design 81, 20-22 (2006) 2305-2313
- L. Wegener, Status of Wendelstein 7-X construction, Fusion Engineering and Design 84, 2-6 (2009) 106-112
- H.-S. Bosch et al, Construction of Wendelstein 7-X; Engineering a Steady-State Stellarator, IEEE Trans. Plasma Science 38, 3 (2010) 265
- H.-S. Bosch et al, Technical challenges in the construction of the steady-state stellarator Wendelstein 7-X, Nucl. Fusion 53 (2013) 126001
- D. Clery, Feature: The bizarre reactor that might save nuclear fusion, Science, 21 October 2015
- O. Neubauer et al, Diagnostic setup for investigation of plasma wall interactions at Wendelstein 7-X, Fusion Engineering and Design 96-97 (2015) 891-894
- T. Sunn Pedersen et al, Plans for the first plasma operation of Wendelstein 7-X, Nucl. Fusion 55 (2015) 126001
- M. Krychowiak et al, Overview of diagnostic performance and results for the first operation phase in Wendelstein 7-X, Review of Scientific Instruments 87 (2016) 11D304
- R.C. Wolf et al, Major results from the first plasma campaign of the Wendelstein 7-X stellarator, Nucl. Fusion 57 (2017) 102020
- D. Hathiramani et al, Upgrades of edge, divertor and scrape-off layer diagnostics of W7‐X for OP1.2, Fusion Engineering and Design 136A (2018) 304-308
- A. Dinklage et al, Magnetic configuration effects on the Wendelstein 7-X stellarator, Nature Phys 14 (2018) 855–860
- R.C. Wolf et al, Performance of Wendelstein 7-X stellarator plasmas during the first divertor operation phase, Physics of Plasmas 26 (2019) 082504