TJ-II:Helium Beam: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[TJ-II]] possesses a supersonic Helium beam diagnostic. | |||
The beam source consists of a fast-pulsed piezoelectric valve with a nozzle of | |||
[[TJ-II]] possesses a supersonic Helium beam diagnostic | 0.3 mm diameter and a parabolic profile skimmer with a diameter | ||
of 0.5 mm. | |||
The mean beam velocity is 1500 m/s. | |||
The density of He atoms at the measurement region is estimated to be of | |||
the order of < 10<sup>11</sup> cm<sup>-3</sup>. | |||
Three He emission lines (667.2, 706.5 and | |||
728.1 nm) are simultaneously detected by means of a beam-splitter system and a set of three 16-channel photomultiplier arrays | |||
(Hamamatsu, model R5900U-20-L16) with interference filters | |||
(FWHM = 1 nm). | |||
<ref>[http://link.aip.org/link/?RSINAK/72/602/1 B. Brañas et al., ''Atomic beam diagnostics for characterization of edge plasma in TJ-II stellarator'', Rev. Sci. Instrum. '''72''', 602 (2001)]</ref> | <ref>[http://link.aip.org/link/?RSINAK/72/602/1 B. Brañas et al., ''Atomic beam diagnostics for characterization of edge plasma in TJ-II stellarator'', Rev. Sci. Instrum. '''72''', 602 (2001)]</ref> | ||
A Collisional Radiative (CR) model for the line emission intensity ratios is used | |||
to deduce electron densities and temperatures. | |||
<ref>[http://link.aip.org/link/?RSINAK/75/3478/1 A. Hidalgo et al., ''Multipulse supersonic helium beam diagnostic in the TJ-II stellarator'', Rev. Sci Instrum. '''75''', 3478 (2004)]</ref> | <ref>[http://link.aip.org/link/?RSINAK/75/3478/1 A. Hidalgo et al., ''Multipulse supersonic helium beam diagnostic in the TJ-II stellarator'', Rev. Sci Instrum. '''75''', 3478 (2004)]</ref> | ||
<ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2009.01.290 F. Guzmán et al, ''On the determination of edge Ti profiles by a supersonic He beam in TJ-II'', Journal of Nuclear Materials '''390-391''' (2009) 1127-1130]</ref> | <ref name="Guzman">[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2009.01.290 F. Guzmán et al, ''On the determination of edge Ti profiles by a supersonic He beam in TJ-II'', Journal of Nuclear Materials '''390-391''' (2009) 1127-1130]</ref> | ||
It provides profiles of the electron temperature and density in the plasma edge at a repetition rate of up to 200 Hz. | It provides profiles of the electron temperature and density in the plasma edge at a repetition rate of up to 200 Hz. | ||
It is located at φ = 355.3° ([[TJ-II:Sectors|sector]] C8). | It is located at φ = 355.3° ([[TJ-II:Sectors|sector]] C8). | ||
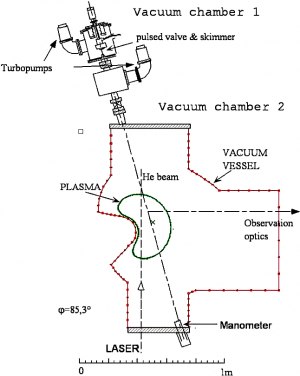
[[File:TJ-II_Helium_beam.png|300px|thumb|right|The TJ-II Helium beam diagnostic. The laser can be crossed with the Helium beam for LiF measurements of the excited He population <ref name="Guzman" /> and validation of the CR model.]] | |||
== Data description == | == Data description == | ||
Revision as of 11:17, 29 August 2010
TJ-II possesses a supersonic Helium beam diagnostic. The beam source consists of a fast-pulsed piezoelectric valve with a nozzle of 0.3 mm diameter and a parabolic profile skimmer with a diameter of 0.5 mm. The mean beam velocity is 1500 m/s. The density of He atoms at the measurement region is estimated to be of the order of < 1011 cm-3. Three He emission lines (667.2, 706.5 and 728.1 nm) are simultaneously detected by means of a beam-splitter system and a set of three 16-channel photomultiplier arrays (Hamamatsu, model R5900U-20-L16) with interference filters (FWHM = 1 nm). [1] A Collisional Radiative (CR) model for the line emission intensity ratios is used to deduce electron densities and temperatures. [2] [3] It provides profiles of the electron temperature and density in the plasma edge at a repetition rate of up to 200 Hz.
It is located at φ = 355.3° (sector C8).
Data description
The Helium beam pulse shape is stored in the TJ-II database with the name 'HELIO_HAZ'. The detected line emission signals are stored with the names 'He_xxx_yy', where 'xxx' is the wavelength in nm (667, 706, or 728), while 'yy' is the position (from 01 through 16).
References
- ↑ B. Brañas et al., Atomic beam diagnostics for characterization of edge plasma in TJ-II stellarator, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 72, 602 (2001)
- ↑ A. Hidalgo et al., Multipulse supersonic helium beam diagnostic in the TJ-II stellarator, Rev. Sci Instrum. 75, 3478 (2004)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 F. Guzmán et al, On the determination of edge Ti profiles by a supersonic He beam in TJ-II, Journal of Nuclear Materials 390-391 (2009) 1127-1130