TJ-II:Heavy Ion Beam Probe: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
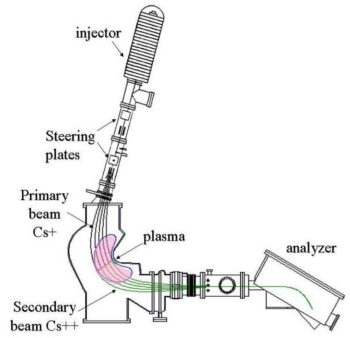
The advanced Heavy Ion Beam Probe can simulataneously measure the plasma electric potential ''φ'', the electron density ''n<sub>e</sub>'', the electron temperature ''T<sub>e</sub>'', and a poloidal magnetic field component ''B<sub>p</sub>'' at a point inside the plasma. | The advanced Heavy Ion Beam Probe can simulataneously measure the plasma electric potential ''φ'', the electron density ''n<sub>e</sub>'', the electron temperature ''T<sub>e</sub>'', and a poloidal magnetic field component ''B<sub>p</sub>'' at a point inside the plasma. | ||
<ref>L.I. Krupnik et al., Fusion Engineering and Design '''56-57''' (2001) 935</ref> | <ref>L.I. Krupnik et al., Fusion Engineering and Design '''56-57''' (2001) 935</ref> | ||
<ref>I.S. Bondarenko et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. '''72''', 583 (2001)</ref> | <ref>[http://link.aip.org/link/?RSINAK/72/583/1 I.S. Bondarenko et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. '''72''', 583 (2001)]</ref> | ||
This point can be scanned through the plasma cross-section by varying the deflection potentials (active beam control). | This point can be scanned through the plasma cross-section by varying the deflection potentials (active beam control). | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 12:22, 17 July 2009
The advanced Heavy Ion Beam Probe can simulataneously measure the plasma electric potential φ, the electron density ne, the electron temperature Te, and a poloidal magnetic field component Bp at a point inside the plasma. [1] [2] This point can be scanned through the plasma cross-section by varying the deflection potentials (active beam control).
References
- ↑ L.I. Krupnik et al., Fusion Engineering and Design 56-57 (2001) 935
- ↑ I.S. Bondarenko et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 72, 583 (2001)