ITER
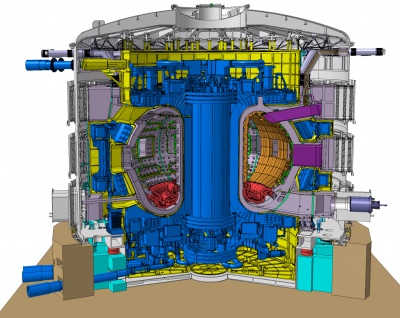
ITER is an international engineering and research project oriented towards demonstrating the technical and scientific viability of fusion as an energy source. For general background information on the project, refer to the Wikipedia.
Main specifications
ITER is a magnetic confinement device of the tokamak type, with the following characteristics in the reference scenario: [1] [2]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Major radius, R0(m) | 6.2 |
| Minor radius, a (m) | 2.0 |
| Toroidal field at R0, BT (T) | 5.3 |
| Plasma current, Ip (MA) | 15 |
| Edge safety factor, q95 | 3.0 |
| Confinement enhancement, HH98(y,2) | 1.0 |
| Normalised beta, βN | 1.8 |
| Average electron density, <ne> (1019m-3) | 10.1 |
| Fraction of Greenwald limit, <ne>/nGW | 0.85 |
| Average ion temperature, <Ti> (keV) | 8.0 |
| Average electron temperature, <Te> (keV) | 8.8 |
| Neutral beam power, PNB (MW) | 33 |
| RF power, PRF (MW) | 7 |
| Fusion power, Pfusion (MW) | 400 |
| Fusion gain, Q=Pfusion/(PNB+PRF) | 10 |
| Non inductive current fraction, INI/Ip (%) | 28 |
| Burn time (s) | 400 |