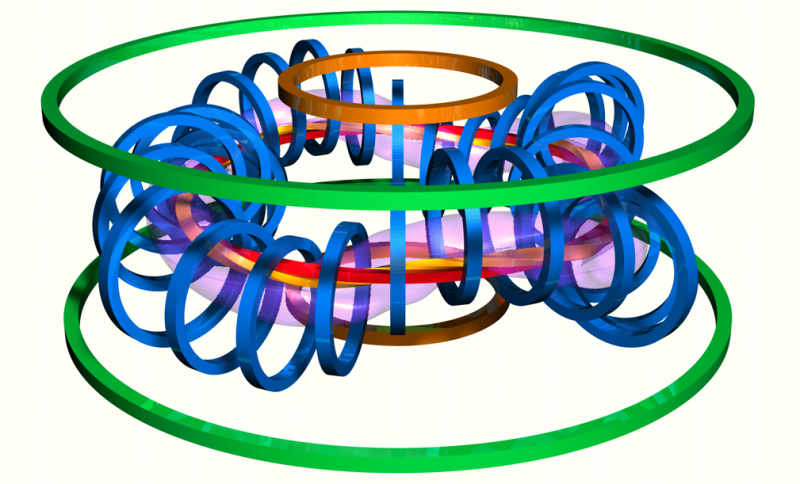
TJ-II:Coil system
The TJ-II coil system is listed in the table below (in cylindrical coordinates). All coils are circular, except the helical coil. They are directly cooled by water flowing trough longitudinal holes in the conductors. All coils have a reinforced structure to avoid mechanical deformations.[1]
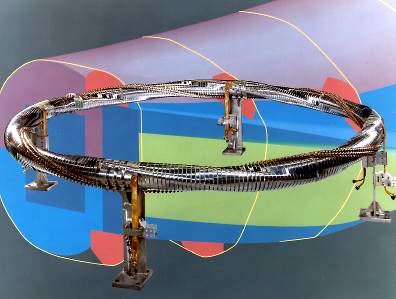
| Coil | Number | Size (m) | Position (m) | Turns |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular (CC) | 1 | R = 1.5 | Z = 0 | 24 |
| Helical (HX)[2] | 1 | R = 1.5 swing = 0.07 |
Z = 0 | 24 |
| Toroidal (TF) | 28 | r = 0.425 | R = 1.5 + 0.2825 cos(4φ) Z = -0.2825 sin(4φ) |
8 |
| Toroidal (TF) | 4 | r = 0.475 | R = 1.5 + 0.3325 cos(4φ) Z = -0.3325 sin(4φ) φ = 0, 90, 180, 270° |
9 |
| Vertical (VF) | 2 | R = 2.25 | Z = ± 0.75 | 16 |
| Compensation (OH) | 2 | R = 0.78 | Z = ± 0.75 | 20 |
| Compensation (OH) | 2 | R = 2.29 | Z = ± 0.75 | 1 |
| Radial (R) | 2 | R = 0.74 | Z = ± 0.75 | 7 |
| Radial (R) | 2 | R = 2.24 | Z = ± 0.75 | 5 |
The main helical field is produced by the CC, HX, and TF coils. The vertical field coils (VF) allow positioning the magnetic axis. The ohmic coils (OH) can generate a loop voltage of 0.1 V, intended to cancel spurious toroidal currents. The radial coils (R) produce a trimming radial field of up to 100 G, intended to compensate stray fields.
See also
References
- ↑ M. Medrano, M. Blaumoser, J. Alonso, G. Barrera, M. Pastor, C. Rubio, F. Pedrazo, and O. Heusmann, Strength considerations on the magnetic field coils of the Spanish Stellarator TJ-II, Fusion Engineering, 15th IEEE/NPSS Symposium (1993)
- ↑ J. Alonso and M. Blaumoser, Design and feasibility of the TJ-II hard core, Fusion Engineering, 14th IEEE/NPSS Symposium (1991)