Sawtooth: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
The name is due to the characteristic [[Wikipedia:Sawtooth wave|waveform]] of many diagnostic signals. | The name is due to the characteristic [[Wikipedia:Sawtooth wave|waveform]] of many diagnostic signals. | ||
The reconnection leads to the rapid expulsion of energy from a central region (usually contained with the ''q'' = 1 rational surface). | The reconnection leads to the rapid expulsion of energy from a central region (usually contained with the [[Safety factor|''q'' = 1]] rational surface). | ||
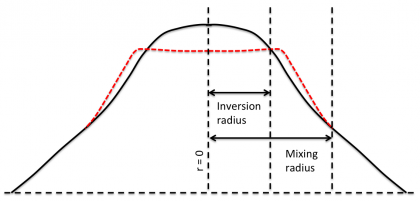
The region in which the temperature goes down during the crash is bounded by the inversion radius (see figure). | The region in which the temperature goes down during the crash is bounded by the inversion radius (see figure). | ||
This leads to the fast increase of energy content in an annular region surrounding the central region. | This leads to the fast increase of energy content in an annular region surrounding the central region. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:07, 29 September 2018
A sawtooth is a magnetic reconnection phenomenon occurring in many tokamak plasmas. The name is due to the characteristic waveform of many diagnostic signals.
The reconnection leads to the rapid expulsion of energy from a central region (usually contained with the q = 1 rational surface). The region in which the temperature goes down during the crash is bounded by the inversion radius (see figure). This leads to the fast increase of energy content in an annular region surrounding the central region. The region where the temperature goes up during the crash is bounded by the inversion radius and the mixing radius (see figure).