TJ-II:Coil system: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
The [[TJ-II]] coil system is listed in the table below. | The [[TJ-II]] coil system is listed in the table below. | ||
All coils are directly [[TJ-II:Cooling system|cooled]] by water flowing trough longitudinal holes in the conductors. | All coils are directly [[TJ-II:Cooling system|cooled]] by water flowing trough longitudinal holes in the conductors. | ||
All coils have a reinforced structure to avoid mechanical deformations. | All coils have a reinforced structure to avoid mechanical deformations.<ref>M. Medrano, M. Blaumoser, J. Alonso, G. Barrera, M. Pastor, C. Rubio, F. Pedrazo, and O. Heusmann, ''Strength considerations on the magnetic field coils of the Spanish Stellarator TJ-II'', [[doi:10.1109/FUSION.1993.518529| Fusion Engineering, 15th IEEE/NPSS Symposium (1993)]]</ref> | ||
{| class="wikitable" align="center" border="1" | {| class="wikitable" align="center" border="1" | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|Circular (CC) || 1 || ''R'' = 1.5 || 24 | |Circular (CC) || 1 || ''R'' = 1.5 || 24 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Helical (HX) || 1 || ''R'' = 1.5 <br> swing = 0.07 || 24 | |Helical (HX)<ref>J. Alonso and M. Blaumoser, ''Design and feasibility of the TJ-II hard core'', [[doi:10.1109/FUSION.1991.218810|Fusion Engineering, 14th IEEE/NPSS Symposium (1991)]]</ref> || 1 || ''R'' = 1.5 <br> swing = 0.07 || 24 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Toroidal (TF) || 28 || ''r'' = 0.425 || 8 | |Toroidal (TF) || 28 || ''r'' = 0.425 || 8 | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
* [[TJ-II:Power supply]] | * [[TJ-II:Power supply]] | ||
* [[TJ-II:Magnetic field]] | * [[TJ-II:Magnetic field]] | ||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
Revision as of 13:22, 30 May 2018
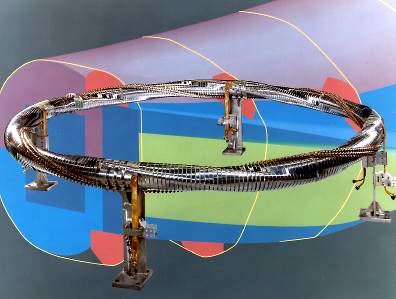
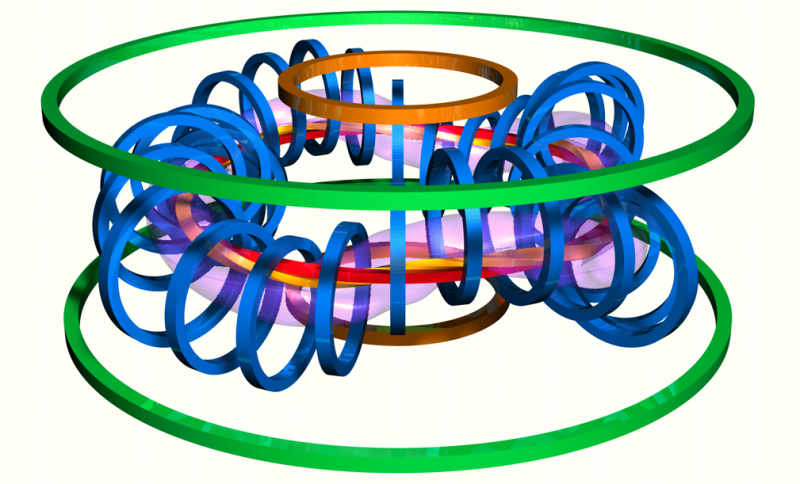
The TJ-II coil system is listed in the table below. All coils are directly cooled by water flowing trough longitudinal holes in the conductors. All coils have a reinforced structure to avoid mechanical deformations.[1]
| Coil | Number | Size (m) | Turns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circular (CC) | 1 | R = 1.5 | 24 |
| Helical (HX)[2] | 1 | R = 1.5 swing = 0.07 |
24 |
| Toroidal (TF) | 28 | r = 0.425 | 8 |
| Toroidal (TF) | 4 | r = 0.475 | 9 |
| Vertical (VF) | 2 | R = 2.25 | 16 |
| Compensation (OH) | 2 | R = 0.78 | 20 |
| Compensation (OH) | 2 | R = 2.29 | 1 |
| Radial (R) | 2 | R = 0.74 | 7 |
| Radial (R) | 2 | R = 2.24 | 5 |
The main helical field is produced by the CC, HX, and TF coils. The vertical field coils (VF) allow positioning the magnetic axis. The ohmic coils (OH) can generate a loop voltage of 0.1 V, intended to cancel spurious toroidal currents. The radial coils (R) produce a trimming radial field of up to 100 G, intended to compensate stray fields.
See also
References
- ↑ M. Medrano, M. Blaumoser, J. Alonso, G. Barrera, M. Pastor, C. Rubio, F. Pedrazo, and O. Heusmann, Strength considerations on the magnetic field coils of the Spanish Stellarator TJ-II, Fusion Engineering, 15th IEEE/NPSS Symposium (1993)
- ↑ J. Alonso and M. Blaumoser, Design and feasibility of the TJ-II hard core, Fusion Engineering, 14th IEEE/NPSS Symposium (1991)