TJ-II:Neutral Beam Injection: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:TJ-II_NBI.png|500px|thumb|right|Diagram of an NBI injector, coupled to TJ-II]] | |||
[[TJ-II]] disposes of two neutral beam injectors (NBI), each of | [[TJ-II]] disposes of two neutral beam injectors (NBI), each of | ||
which can produce ≤ 300 ms pulses of neutral hydrogen | which can produce ≤ 300 ms pulses of neutral hydrogen | ||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
m<sup>-3</sup>. | m<sup>-3</sup>. | ||
<ref>[http://www.new.ans.org/store/j_75 J. Guasp, M. Liniers, C. Fuentes, and G. Barrera, ''Thermal load calculations at TJ-II vacuum vessel under NBI,'' Fusion Tech., '''35''', pp. 32-41 (1999)]</ref> | <ref>[http://www.new.ans.org/store/j_75 J. Guasp, M. Liniers, C. Fuentes, and G. Barrera, ''Thermal load calculations at TJ-II vacuum vessel under NBI,'' Fusion Tech., '''35''', pp. 32-41 (1999)]</ref> | ||
<ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2005.06.315 C. Fuentes et al, ''Neutral beam injection optimization at TJ-II'', Fusion Engineering and Design '''74''', Issues 1-4 (2005) 249-253]</ref> | <ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2005.06.315 C. Fuentes et al, ''Neutral beam injection optimization at TJ-II'', Fusion Engineering and Design '''74''', Issues 1-4 (2005) 249-253]</ref> | ||
<ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2007.07.054 C. Fuentes et al, ''Power transmission of the neutral beam heating beams at TJ-II'', Fusion Engineering and Design '''82''', Issues 5-14 (2007) 926-932]</ref> | <ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2007.07.054 C. Fuentes et al, ''Power transmission of the neutral beam heating beams at TJ-II'', Fusion Engineering and Design '''82''', Issues 5-14 (2007) 926-932]</ref> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
NBI2 is located in [[TJ-II:Sectors|sector]] C1. | NBI2 is located in [[TJ-II:Sectors|sector]] C1. | ||
[[ | === Power supply === | ||
The two high voltage power supplies feeding the acceleration grids of the injectors are of the transformer–rectifier type, taking their primary energy from a pulsed [[TJ-II:Power supply|flywheel generator]], and are coupled to the acceleration grids through a switching device. | |||
<ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0920-3796(01)00389-1 J. Alonso et al, ''High voltage power supplies for the neutral beam injectors of the stellarator TJ-II'', Fusion Engineering and Design '''56-57''' (2001) 693-697]</ref> | |||
=== Control system === | |||
The NBI system has its own control system. | |||
<ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0920-3796(01)00349-0 L. Martínez-Laso et al, ''TJ-II neutral beam injectors control and data acquisition system'', Fusion Engineering and Design '''56-57''' (2001) 477-480]</ref> | |||
<ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2006.04.014 R. Carrasco et al, ''The NBI control system for the TJ-II'', Fusion Engineering and Design '''81''', Issues 15-17 (2006) 1813-1816]</ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 20:40, 23 September 2009
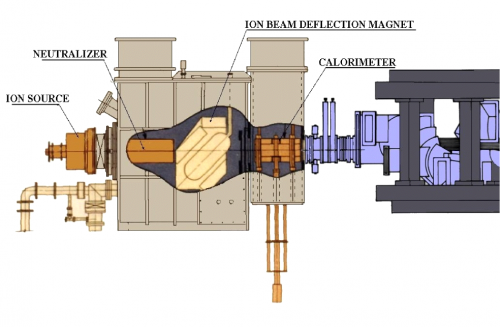
TJ-II disposes of two neutral beam injectors (NBI), each of which can produce ≤ 300 ms pulses of neutral hydrogen accelerated to 40 keV, to provide up to 1.2 MW of absorbed additional heating for central electron densities up to 1.6×1020 m-3. [1] [2] [3]
NBI1 is located in sector D8. NBI2 is located in sector C1.
Power supply
The two high voltage power supplies feeding the acceleration grids of the injectors are of the transformer–rectifier type, taking their primary energy from a pulsed flywheel generator, and are coupled to the acceleration grids through a switching device. [4]
Control system
The NBI system has its own control system. [5] [6]
References
- ↑ J. Guasp, M. Liniers, C. Fuentes, and G. Barrera, Thermal load calculations at TJ-II vacuum vessel under NBI, Fusion Tech., 35, pp. 32-41 (1999)
- ↑ C. Fuentes et al, Neutral beam injection optimization at TJ-II, Fusion Engineering and Design 74, Issues 1-4 (2005) 249-253
- ↑ C. Fuentes et al, Power transmission of the neutral beam heating beams at TJ-II, Fusion Engineering and Design 82, Issues 5-14 (2007) 926-932
- ↑ J. Alonso et al, High voltage power supplies for the neutral beam injectors of the stellarator TJ-II, Fusion Engineering and Design 56-57 (2001) 693-697
- ↑ L. Martínez-Laso et al, TJ-II neutral beam injectors control and data acquisition system, Fusion Engineering and Design 56-57 (2001) 477-480
- ↑ R. Carrasco et al, The NBI control system for the TJ-II, Fusion Engineering and Design 81, Issues 15-17 (2006) 1813-1816