OLMAT: Difference between revisions
Created page with "The OLMAT (Optimization of liquid targets) facility at the Laboratorio Nacional de Fusión is aimed at testing LM (Liquid Metal) prototypes under DEMO-relevant heat loads <ref>Alegre D., Oyarzabal E., Tafalla D., Liniers M., Soleto A. and Tabarés F.L. (2020) ''Design and testing of advanced liquid metal targets for DEMO divertor: the OLMAT project''. J. Fusion Energy 39 411</ref>. File:OLMAT.jpg|400px|thumb|right|CAD design of..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The OLMAT (Optimization of | The OLMAT (Optimization of Liquid Metal Targets) facility at the [[Laboratorio Nacional de Fusión]] is aimed at testing LM (Liquid Metal) prototypes under DEMO-relevant heat loads <ref>Alegre D., Oyarzabal E., Tafalla D., Liniers M., Soleto A. and Tabarés F.L. (2020) ''Design and testing of advanced liquid metal targets for DEMO divertor: the OLMAT project''. [[doi:10.1007/s10894-020-00254-5|J. Fusion Energy 39 411]]</ref>. | ||
[[File:OLMAT.jpg|400px|thumb|right|CAD design of OLMAT. (a) irradiation chamber; (b) valve to NBI; (c) valve to TJ-II; (d) pre-chamber for sample loading; (e) sample insertion system; (f) upper turbopump with liquid metal condensation bafflers; (g) BaF2 optical window for infrared thermography; (h) diagnostic ports and windows.]] | [[File:OLMAT.jpg|400px|thumb|right|CAD design of OLMAT. (a) irradiation chamber; (b) valve to NBI; (c) valve to TJ-II; (d) pre-chamber for sample loading; (e) sample insertion system; (f) upper turbopump with liquid metal condensation bafflers; (g) BaF2 optical window for infrared thermography; (h) diagnostic ports and windows.]] | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Moreover, the NBI beam is wide enough to irradiate large samples (<20 cm diameter), allowing redeposition studies of the eroded and evaporated material. | Moreover, the NBI beam is wide enough to irradiate large samples (<20 cm diameter), allowing redeposition studies of the eroded and evaporated material. | ||
In a second stage of the project a Q-CW, high-power fibre laser is used to simulate ELM-like powers in a small area, or the strike point power deposition profile. | In a second stage of the project a Q-CW, high-power fibre laser is used to simulate ELM-like powers in a small area, or the strike point power deposition profile. | ||
[[File:OLMAT1.png|500px|thumb|center|The OLMAT facility and TJ-II]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:47, 1 May 2024
The OLMAT (Optimization of Liquid Metal Targets) facility at the Laboratorio Nacional de Fusión is aimed at testing LM (Liquid Metal) prototypes under DEMO-relevant heat loads [1].
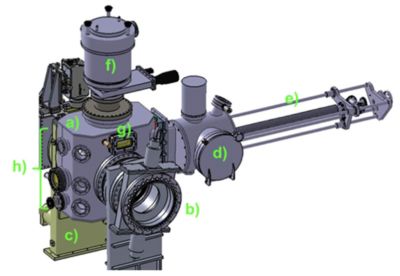
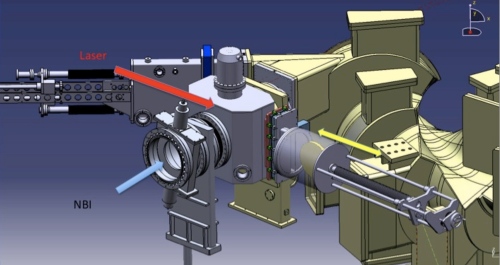
It is based on the use of the neutral beam injectors (NBI) of the TJ-II stellarator for the irradiation of LM targets (mainly CPS) at DEMO-relevant powers. The characteristics of the NBI beam are adequate for the simulation of steady state and slow transient powers (10–20 MW m−2) including vapour shielding and fatigue studies. Moreover, the NBI beam is wide enough to irradiate large samples (<20 cm diameter), allowing redeposition studies of the eroded and evaporated material. In a second stage of the project a Q-CW, high-power fibre laser is used to simulate ELM-like powers in a small area, or the strike point power deposition profile.
References
- ↑ Alegre D., Oyarzabal E., Tafalla D., Liniers M., Soleto A. and Tabarés F.L. (2020) Design and testing of advanced liquid metal targets for DEMO divertor: the OLMAT project. J. Fusion Energy 39 411