TJ-II:Diagnostic neutral beam: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:TJ-II DNBI.jpg|500px|thumb|right|Diagram of the TJ-II Diagnostic Neutral Beam Injector ]] | [[File:TJ-II DNBI.jpg|500px|thumb|right|Diagram of the TJ-II Diagnostic Neutral Beam Injector]] | ||
[[TJ-II]] | [[TJ-II]] is equipped with a compact diagnostic neutral beam injector, designed for performing spatially resolved Charge-exchange Recombination Spectroscopy (CXRS) and Motional Stark Effect (MSE) measurements. It is located in [[TJ-II:Sectors|sector]] A7 and it is employed to obtain either measure radial profiles of impurity ion (carbon) temperature and velocity (CXRS) or to measure the wavelength separation of the Stark splitting of beam hydrogen atom emissions at 656.3 nm (these emissions are Doppler shifted in wavelength to about 660 nm). | ||
<ref> | <ref>K.J. McCarthy et al, ''Diagnostic neutral beam injector and associated diagnostic systems for the TJ-II stellarator device'', [[doi:10.1063/1.1784512|Rev. Sci. Instrum. '''75''', 3499 (2004)]]</ref> | ||
The injector, an upgraded DINA-5 model, is supported on a mobile cradle that permits its path through the plasma to be varied by ±3° poloidally. In parallel, a dedicated bidirectional (two vertical opposing views plus a single toroidal view) multichannel spectroscopic diagnostic, incorporating fiber arrays, an f/1.8 spectrograph, and a back-illuminated charge-coupled device, is installed to obtain Doppler line shifts and widths (around 529.2 nm) with ~1 cm spatial resolution for CXRS | |||
<ref>J.M. Carmona et al, ''Charge-exchange spectroscopic diagnostic for the TJ-II stellarator'', [[doi:10.1063/1.2229200|Rev. Sci. Instrum. '''77''', 10F107 (2006)]]</ref> | |||
<ref>J.M. Carmona et al, ''Density Dependence of Ion Temperature Measured by Active Charge-Exchange Spectroscopy in ECRH Plasmas of the TJ-II Stellarator'', [[doi:10.13182/FST08-A1911|Fusion Science and Technology '''54''', 4 (2008) 962-969]]</ref> or wavelength separations. | |||
When the Diagnostic Neutral Beam Injector is used for Motional Stark Effect, it is possible to obtain the magnitude and pitch of components of the magnetic field<ref>K. J. McCarthy, N. Panadero, A. López-Fraguas, J. Hernández, and B. van Milligen, ''A Spectrally Resolved Motional Stark Effect Diagnostic for the TJ-II Stellarator'', [[doi:10.1002/ctpp.201400067|Contrib. Plasma Phys. 55, No. 6 (2015) 459]]</ref>. | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[TJ-II:Compact Neutral Particle Analyzer|Compact Neutral Particle Analyzer]] | |||
* [[TJ-II:Charge exchange spectroscopy|Charge exchange spectroscopy]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:35, 12 July 2025
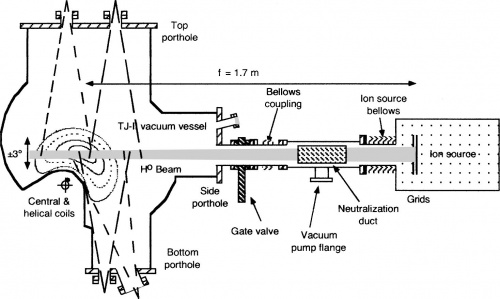
TJ-II is equipped with a compact diagnostic neutral beam injector, designed for performing spatially resolved Charge-exchange Recombination Spectroscopy (CXRS) and Motional Stark Effect (MSE) measurements. It is located in sector A7 and it is employed to obtain either measure radial profiles of impurity ion (carbon) temperature and velocity (CXRS) or to measure the wavelength separation of the Stark splitting of beam hydrogen atom emissions at 656.3 nm (these emissions are Doppler shifted in wavelength to about 660 nm). [1] The injector, an upgraded DINA-5 model, is supported on a mobile cradle that permits its path through the plasma to be varied by ±3° poloidally. In parallel, a dedicated bidirectional (two vertical opposing views plus a single toroidal view) multichannel spectroscopic diagnostic, incorporating fiber arrays, an f/1.8 spectrograph, and a back-illuminated charge-coupled device, is installed to obtain Doppler line shifts and widths (around 529.2 nm) with ~1 cm spatial resolution for CXRS [2] [3] or wavelength separations.
When the Diagnostic Neutral Beam Injector is used for Motional Stark Effect, it is possible to obtain the magnitude and pitch of components of the magnetic field[4].
See also
References
- ↑ K.J. McCarthy et al, Diagnostic neutral beam injector and associated diagnostic systems for the TJ-II stellarator device, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75, 3499 (2004)
- ↑ J.M. Carmona et al, Charge-exchange spectroscopic diagnostic for the TJ-II stellarator, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, 10F107 (2006)
- ↑ J.M. Carmona et al, Density Dependence of Ion Temperature Measured by Active Charge-Exchange Spectroscopy in ECRH Plasmas of the TJ-II Stellarator, Fusion Science and Technology 54, 4 (2008) 962-969
- ↑ K. J. McCarthy, N. Panadero, A. López-Fraguas, J. Hernández, and B. van Milligen, A Spectrally Resolved Motional Stark Effect Diagnostic for the TJ-II Stellarator, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 55, No. 6 (2015) 459