Divertor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with 'A divertor configuration is a magnatic field configuration by which the toroidally confined (plasma) region is separated from the outside world by a separatrix - a…' |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A divertor configuration is a | [[File:Divertors.png|300px|thumb|right|Sketch of divertor types: single and double null tokamak divertors (toroidally symmetric), and island divertor. From <ref name="Feng">[http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0029-5515/46/8/006 Y. Feng, F. Sardei, P. Grigull, K. McCormick, J. Kisslinger and D. Reiter, ''Physics of island divertors as highlighted by the example of W7-AS'', Nucl. Fusion '''46''' (2006) 807]</ref>.]] | ||
as opposed to a limiter configuration | A divertor configuration is a magnetic field configuration in which the toroidally confined (plasma) region is separated from the outside world by a [[Separatrix|separatrix]] - | ||
as opposed to a limiter configuration in which the plasma's Last Closed Magnetic Surface is determined by the intersection of field lines by a material object. | |||
The divertor | One can distinguish '[[Tokamak|tokamak]] divertors' (characterised by toroidal symmetry and one or two X-points or 'nulls') and '[[Island Divertor|island divertors]]' (for [[Stellarator|stellarators]]). | ||
<ref name="Feng"></ref> | |||
The term 'divertor' can refer to: | |||
* the magnetic field structure beyond the X-point and in contact with material surfaces, or | |||
* the material structure intersecting the 'outgoing legs' of the magnetic separatrix surface. | |||
The divertor region between the 'outgoing legs' - the region between the material divertor and the X-point, up to the separatrix - is known as the private flux region (PFR). | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Flux surface]] | * [[Flux surface]] | ||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
Latest revision as of 08:12, 6 April 2023
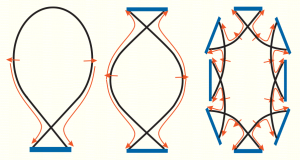
A divertor configuration is a magnetic field configuration in which the toroidally confined (plasma) region is separated from the outside world by a separatrix - as opposed to a limiter configuration in which the plasma's Last Closed Magnetic Surface is determined by the intersection of field lines by a material object.
One can distinguish 'tokamak divertors' (characterised by toroidal symmetry and one or two X-points or 'nulls') and 'island divertors' (for stellarators). [1]
The term 'divertor' can refer to:
- the magnetic field structure beyond the X-point and in contact with material surfaces, or
- the material structure intersecting the 'outgoing legs' of the magnetic separatrix surface.
The divertor region between the 'outgoing legs' - the region between the material divertor and the X-point, up to the separatrix - is known as the private flux region (PFR).