Divertor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
A divertor configuration is a magnetic field configuration in which the toroidally confined (plasma) region is separated from the outside world by a [[Separatrix|separatrix]] - | A divertor configuration is a magnetic field configuration in which the toroidally confined (plasma) region is separated from the outside world by a [[Separatrix|separatrix]] - | ||
as opposed to a limiter configuration in which the plasma's Last Closed Magnetic Surface is determined by the intersection of field lines by a material object. | as opposed to a limiter configuration in which the plasma's Last Closed Magnetic Surface is determined by the intersection of field lines by a material object. | ||
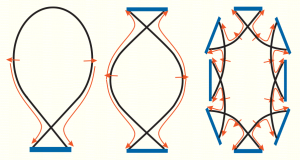
One can distinguish '[[Tokamak|tokamak]] divertors' (characterised by toroidal symmetry and one or two X-points or 'nulls') and 'island divertors' (for stellarators). | One can distinguish '[[Tokamak|tokamak]] divertors' (characterised by toroidal symmetry and one or two X-points or 'nulls') and 'island divertors' (for stellarators). | ||
<ref name="Feng"></ref> | <ref name="Feng"></ref> | ||
The term 'divertor' can either refer to the magnetic field structure (beyond the X-point and in contact with material surfaces) or to the material structure intersecting the 'outgoing legs' of the magnetic separatrix surface. | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 17:20, 15 February 2010

Sketch of divertor types: single and double null tokamak divertors (toroidally symmetric), and island divertor. From [1].
A divertor configuration is a magnetic field configuration in which the toroidally confined (plasma) region is separated from the outside world by a separatrix - as opposed to a limiter configuration in which the plasma's Last Closed Magnetic Surface is determined by the intersection of field lines by a material object.
One can distinguish 'tokamak divertors' (characterised by toroidal symmetry and one or two X-points or 'nulls') and 'island divertors' (for stellarators). [1]
The term 'divertor' can either refer to the magnetic field structure (beyond the X-point and in contact with material surfaces) or to the material structure intersecting the 'outgoing legs' of the magnetic separatrix surface.